Understanding Intraocular Pressure and Eye Health
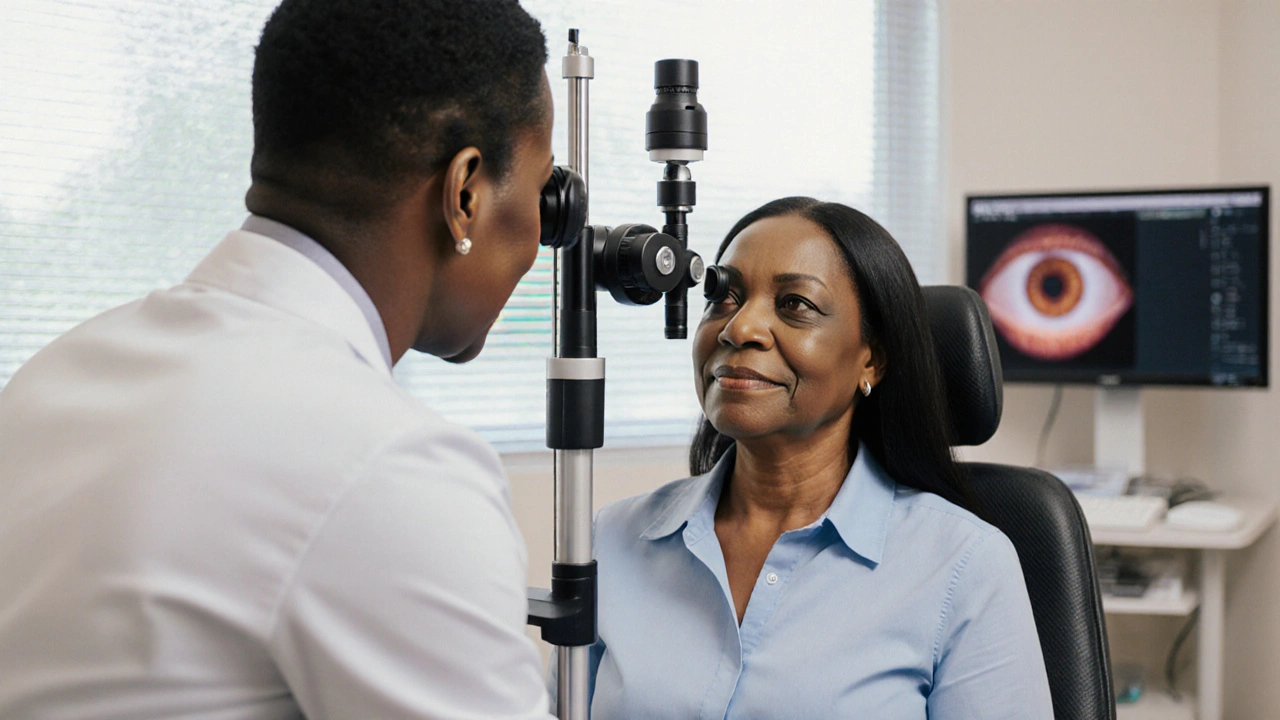
When dealing with intraocular pressure, the fluid pressure inside the eye that keeps its shape and supports nutrient flow. Also known as IOP, it is a key factor in keeping vision stable. If you’ve ever heard doctors ask about "pressure" during an eye exam, they’re really checking this number.
How We Measure Eye Pressure
The most common way to check IOP is through tonometry, a quick test that uses a tiny probe or puff of air to gauge the eye’s pressure. Intraocular pressure readings are given in millimeters of mercury (mmHg). Normal values sit between 10 and 21 mmHg; anything higher can be a warning sign. Modern devices give instant numbers, so eye doctors can spot problems early.
High readings often point toward glaucoma, a group of eye diseases that damage the optic nerve, frequently linked to elevated IOP. When untreated, glaucoma can slowly steal peripheral vision and eventually lead to blindness. That’s why regular checks are a must, especially if you have a family history or other risk factors.
Treatment starts by lowering the pressure. One of the most prescribed options is a class of drops called beta‑blocker eye drops, medications like timolol that reduce fluid production in the eye. They’re often the first line because they work fast and have a good safety record. If beta‑blockers aren’t enough, doctors may add prostaglandin analogs or carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, each working a different way to keep the pressure in check.
Did you know that what you eat and how active you are can affect IOP too? Studies show that a low‑salt diet, regular aerobic exercise, and staying hydrated can help keep pressure stable. Some blood‑pressure medicines, such as certain calcium‑channel blockers, also have the side effect of lowering eye pressure, which can be a bonus for patients with both hypertension and ocular concerns.
For people whose pressure is high but haven’t developed vision loss yet, the term ocular hypertension, elevated IOP without any detectable optic nerve damage is used. Monitoring ocular hypertension closely can prevent it from turning into glaucoma. Many clinics now offer home tonometry kits, letting patients track their numbers between visits and catch spikes early.
Below you’ll find a curated set of articles that dive deeper into the meds, tests, and lifestyle tweaks mentioned here. Whether you’re looking for drug comparisons, buying tips for generics, or ways to manage eye pressure naturally, the collection has practical answers to help you stay on top of your eye health.