Side Effect: What You Need to Know About Medication Reactions
Side effects happen. Some are mild and brief, others can be serious and need fast action. This tag page collects practical articles that explain common reactions, uncommon risks, and real-world tips so you can make smarter choices about medicines.
Start by asking two simple questions: is the symptom new since you started the drug, and is it getting worse? If yes, treat it as a possible side effect. For mild symptoms — mild nausea, loose stools, slight drowsiness — track how long they last and mention them at your next appointment. For red-flag signs — breathing trouble, chest pain, sudden swelling, severe rash, fainting, or confusion — stop the medicine (if safe) and get emergency care right away.
How side effects usually show up
Timing matters. Some reactions show within hours (allergic rashes), some take days or weeks (mood changes, liver issues), and others appear only after months (long-term organ effects). Age, other drugs, alcohol, existing health conditions, and dose all change your risk. That’s why the same medicine can be harmless for one person and risky for another.
Interactions are common. Using multiple prescriptions, supplements, or herbal remedies can create new side effects. If you buy meds online, check that the pharmacy lists active ingredients and warnings. Our site has guides that explain interaction risks for specific drugs, like antidepressants, antibiotics, and heart medicines.
Practical steps if you suspect a side effect
1) Pause and assess. Don’t ignore sudden or severe symptoms. 2) Check the leaflet or our detailed posts for known side effects — for example, our Strattera and Nasonex articles list typical reactions and what users report. 3) Call your prescriber or pharmacist. They can tell you whether to stop, switch dose, or try a different drug. 4) If symptoms are life-threatening, call emergency services immediately.
Want to learn more? Use the article summaries on this tag to pick specific reads: check the Tamiflu piece for antiviral risks, the Ibuprofen article for heart-related concerns, or the antibiotics guide to weigh side effects vs benefits. Each article focuses on real-world outcomes and practical choices, not just clinical lists.
How to read a side-effect report: look for reported frequency (how many people experienced it), severity (mild vs serious), and what the authors recommend. Our posts mix clinical facts with everyday tips — when to watch, when to act, and how to reduce risk (dose changes, timing, or alternative meds).
Lastly, report unexpected reactions. In many countries you can notify national drug safety agencies (like FDA’s MedWatch). Reporting helps build a clearer safety picture for everyone. Browse the linked posts here to get medicine-specific advice that fits your situation — quick, clear, and practical.
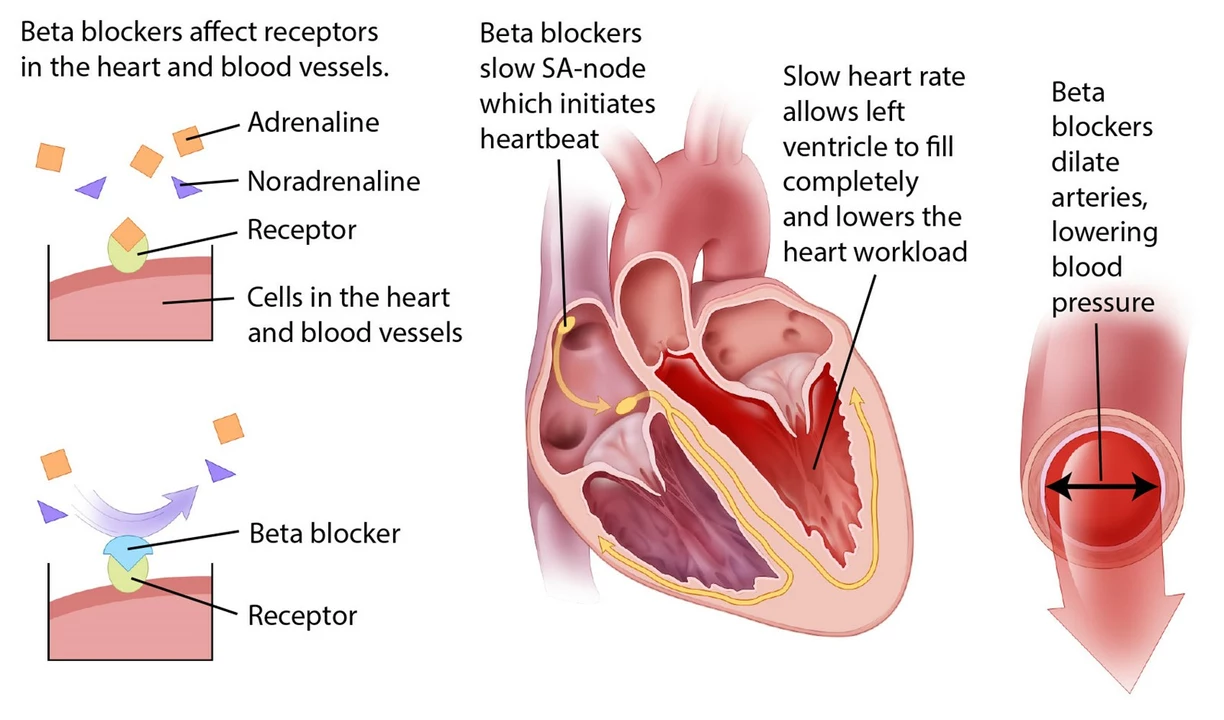
Atenolol and Weakness: Is It a Side Effect?
- 19 Comments
- Apr, 28 2023
I recently came across some information about Atenolol, a medication commonly prescribed for high blood pressure and heart issues. It seems that some users have reported experiencing weakness as a side effect. After doing some research, I've found out that weakness is indeed listed as a potential side effect of Atenolol. If you're taking this medication and experiencing weakness, it's important to discuss this with your healthcare provider. They can help determine if it's related to the medication and suggest possible alternatives or adjustments to your treatment plan.