Flagyl ER vs Alternatives Comparison Tool
Flagyl ER
Pros: Once-daily dosing, good adherence, proven efficacy for BV & trichomoniasis.
Cons: Classic metronidazole-alcohol reaction; slightly higher cost.
Tinidazole
Pros: Shorter course, single dose option.
Cons: Slightly more expensive; limited availability in rural areas.
Clindamycin
Pros: Works when metronidazole is contraindicated, broader anaerobe coverage.
Cons: Higher C. difficile risk, twice-daily dosing.
Doxycycline
Pros: Inexpensive, covers atypical organisms, widely available.
Cons: Sun sensitivity, requires food/water with doses.
Ciprofloxacin
Pros: Excellent for urinary pathogens, once-daily dosing possible.
Cons: Not effective against obligate anaerobes, tendon injury risk.
| Drug | Indication | Dosage Regimen | Duration | Side Effects | Cost (AU$) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flagyl ER | Bacterial vaginosis, Trichomoniasis | 500 mg once daily | 7 days | Nausea, metallic taste, headache | ~30 for 7-day pack |
| Tinidazole | BV, Trichomoniasis, Giardiasis | 500 mg twice daily OR single 2 g dose | 3 days (or single dose) | Metallic taste, dizziness, abdominal pain | ~45 for 3-day pack |
| Clindamycin | PID, anaerobic skin infections | 300 mg twice daily | 7–10 days | Diarrhea (C. difficile risk), nausea | ~55 for 10-day pack |
| Doxycycline | Chlamydia, mixed genital infections | 100 mg twice daily | 7–14 days | Sun sensitivity, esophageal irritation | ~20 for 14-day pack |
| Ciprofloxacin | UTI, gastrointestinal infections | 500 mg twice daily | 5–7 days | Tendon pain, QT prolongation | ~25 for 7-day pack |
Safety Notes
All nitroimidazoles (metronidazole, tinidazole) cause a disulfiram-like reaction if alcohol is consumed within 48 hours of the last dose.
Other key interactions include:
- Warfarin: Metronidazole can increase INR; monitor blood clotting weekly.
- Lithium: Ciprofloxacin may raise lithium levels; check serum levels.
- Oral contraceptives: Some antibiotics lower efficacy; use backup contraception.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding considerations vary by drug; consult a healthcare provider for personalized advice.
Key Takeaways
- Flagyl ER is an extended‑release form of metronidazole designed for once‑daily dosing.
- It’s most effective for bacterial vaginosis, trichomoniasis, and amoebiasis.
- Alternatives such as tinidazole, clindamycin, and doxycycline differ in dosing convenience, side‑effect profile, and cost.
- Choosing the right drug hinges on infection type, patient tolerance, and insurance coverage in Australia.
- Always check for drug interactions - metronidazole and many alternatives can affect alcohol metabolism.
When you’re looking at treatment options for anaerobic infections, the name that often pops up is Flagyl ER. But how does it really stack up against other antibiotics that doctors prescribe? This guide walks you through the science, the practicalities, and the numbers so you can decide whether the extended‑release metronidazole tablet is the best fit for you or if another drug might be smarter.
Flagyl ER is an extended‑release formulation of metronidazole, a nitroimidazole antimicrobial that targets anaerobic bacteria and certain protozoa. It was introduced in Australia in 2019 and quickly became popular because a single 500mg tablet taken once daily can replace the traditional three‑times‑daily regimen of standard metronidazole.
How Flagyl ER Works and When It’s Prescribed
Metronidazole interferes with DNA synthesis in susceptible organisms. By disrupting the electron transport proteins, it creates lethal free radicals that damage bacterial DNA. The extended‑release matrix in Flagyl ER releases the drug steadily over 24hours, maintaining therapeutic plasma levels without the peaks and troughs of immediate‑release tablets.
The drug is approved for:
- Bacterial vaginosis (BV)
- Trichomoniasis
- Amoebic dysentery (caused by Entamoeba histolytica)
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) when anaerobes are suspected
Australian prescribing guidelines (Therapeutic Guidelines: Antibiotic) recommend 500mg once daily for 7days for BV and trichomoniasis, which simplifies adherence compared with the classic 500mg three times daily schedule.
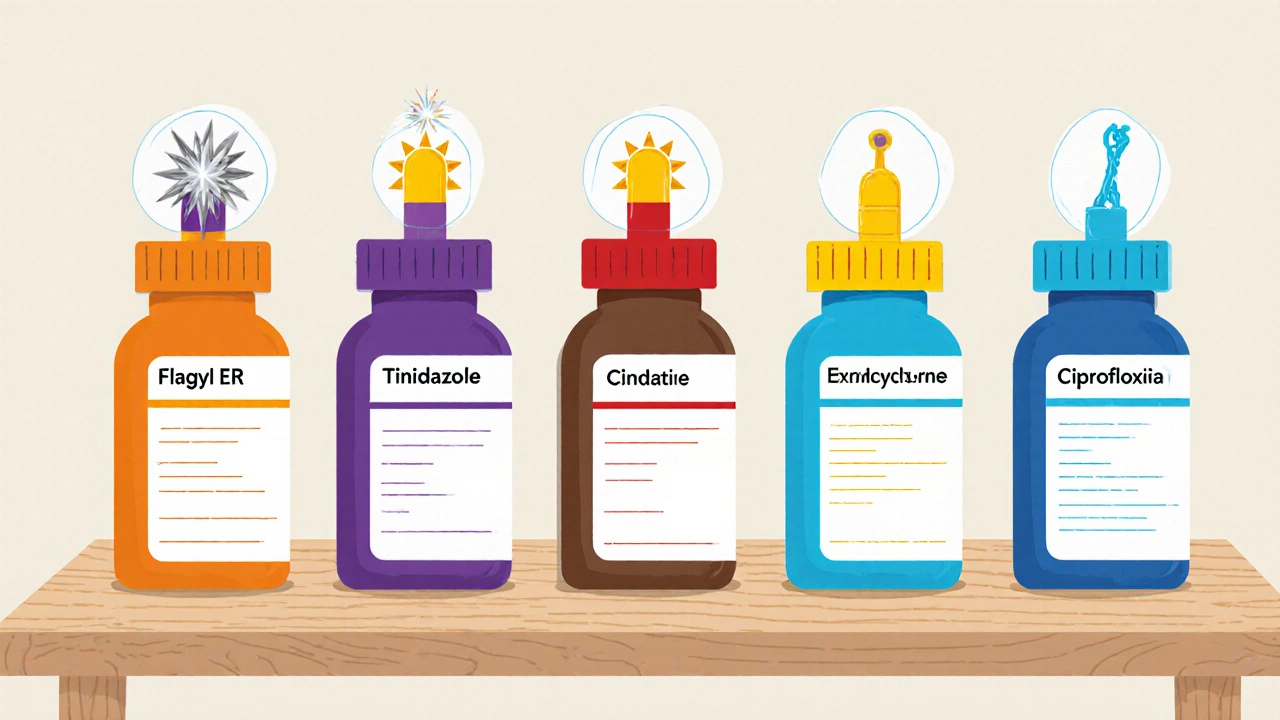
Common Alternatives - Overview
While Flagyl ER is convenient, a few other agents often appear on a clinician’s shortlist. Below are the most frequently considered drugs, each with its own niche.
Tinidazole is another nitroimidazole that offers a shorter course-typically a single 2g dose or 500mg twice daily for 3days. It’s approved for BV, trichomoniasis, and giardiasis.
Clindamycin is a lincosamide antibiotic that targets many anaerobes. It’s often used when metronidazole is contraindicated, such as in patients with severe alcohol‑related liver disease.
Doxycycline is a tetracycline that covers a broad spectrum of atypical organisms, including Chlamydia and Mycoplasma, making it a go‑to for mixed infections.
Ciprofloxacin is a fluoroquinolone used for urinary tract infections and some gastrointestinal infections, but it lacks the anaerobic potency of metronidazole.
Head‑to‑Head Comparison
| Drug | Typical Indication | Dosage Regimen | Treatment Duration | Common Side Effects | Approx. Cost (AU$) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flagyl ER | Bacterial vaginosis, Trichomoniasis | 500mg once daily | 7days | Nausea, metallic taste, headache | ~30 for 7‑day pack |
| Tinidazole | BV, Trichomoniasis, Giardiasis | 500mg twice daily OR single 2g dose | 3days (or single dose) | Metallic taste, dizziness, abdominal pain | ~45 for 3‑day pack |
| Clindamycin | PID, anaerobic skin infections | 300mg twice daily | 7‑10days | Diarrhea (C.difficile risk), nausea | ~55 for 10‑day pack |
| Doxycycline | Chlamydia, mixed genital infections | 100mg twice daily | 7‑14days | Sun sensitivity, esophageal irritation | ~20 for 14‑day pack |
| Ciprofloxacin | UTI, gastrointestinal infections | 500mg twice daily | 5‑7days | Tendon pain, QT prolongation | ~25 for 7‑day pack |
Pros and Cons of Each Option
Below is a quick rundown of what patients typically love or dislike about each drug.
- Flagyl ER
- Pros: once‑daily dosing, good adherence, proven efficacy for BV & trichomoniasis.
- Cons: still causes the classic metronidazole‑alcohol reaction; cost a bit higher than generic metronidazole.
- Tinidazole
- Pros: shorter course, can be given as a single dose for many infections.
- Cons: slightly more expensive; availability can be limited in rural pharmacies.
- Clindamycin
- Pros: works when metronidazole is contraindicated; covers a broader range of anaerobes.
- Cons: higher risk of C.difficile‑associated diarrhea; twice‑daily dosing.
- Doxycycline
- Pros: inexpensive, covers atypical organisms, widely available.
- Cons: needs to be taken with food and water; photosensitivity can be problematic in summer.
- Ciprofloxacin
- Pros: excellent for urinary pathogens; once‑daily dosing possible.
- Cons: not effective against obligate anaerobes; tendon injury risk, especially for athletes.

Choosing the Right Drug for Your Situation
Doctors weigh three core factors: the infecting organism, patient safety, and practicality.
- Infection type: For pure anaerobic infections like BV, Flagyl ER or tinidazole are first‑line. If Chlamydia is also suspected, doxycycline is added.
- Allergy or contraindication: History of severe alcohol‑related liver disease or a known metronidazole hypersensitivity pushes clinicians toward clindamycin.
- Adherence considerations: Busy students or shift workers often prefer the once‑daily Flagyl ER or a single‑dose tinidazole regimen.
Insurance coverage also matters. Many Australian PBS (Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme) listings subsidize flagyl ER for a 7‑day course, while tinidazole may require a private prescription, raising out‑of‑pocket cost.
Safety Tips & Drug Interactions
All nitroimidazoles (metronidazole, tinidazole) cause a disulfiram‑like reaction if alcohol is consumed within 48hours of the last dose. Symptoms include flushing, nausea, vomiting, and palpitations.
Other notable interactions:
- Warfarin: Metronidazole can increase INR; monitor blood clotting weekly.
- Lithium: Ciprofloxacin may raise lithium levels; check serum levels.
- Oral contraceptives: Some antibiotics lower efficacy; use backup contraception.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding considerations:
- Metronidazole (including Flagyl ER) is generally safe in the second and third trimesters, but avoid during the first trimester unless absolutely necessary.
- Clindamycin is also considered low‑risk for lactating mothers.
- Doxycycline is avoided during pregnancy due to tooth staining in the fetus.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I switch from standard metronidazole to Flagyl ER mid‑treatment?
Yes, doctors often convert patients to the extended‑release tablet after the first 24hours to simplify dosing, as long as the total daily dose remains 500mg.
Is the alcohol‑reaction unique to metronidazole?
Both metronidazole and tinidazole cause it; clindamycin and doxycycline do not.
How long after the last dose can I safely drink alcohol?
Wait at least 48hours after finishing Flagyl ER or tinidazole to avoid the disulfiram‑like reaction.
Are there any over‑the‑counter options for BV?
No, BV requires prescription antibiotics. Some probiotic products claim to help restore vaginal flora, but they don’t replace a proper metronidazole course.
What should I do if I experience severe diarrhea while on clindamycin?
Contact your GP immediately. Severe diarrhea could signal C.difficile infection, which requires a different antibiotic like vancomycin.
Bottom line: Flagyl ER offers unrivaled convenience for the most common anaerobic infections, but alternatives like tinidazole, clindamycin, and doxycycline fill important gaps when tolerance, cost, or co‑existing infections come into play. Talk with your pharmacist or doctor about your specific diagnosis, any other meds you’re taking, and your budget to land on the best choice.


Ira Bliss
October 8, 2025 AT 13:31Flagyl ER’s once‑daily dosing truly makes adherence a breeze! 😊
Donny Bryant
October 15, 2025 AT 12:11Flagyl ER indeed simplifies dosing, but remember to avoid alcohol during and after the course. Also, keep an eye on any headache or nausea as they are common side effects.
kuldeep jangra
October 22, 2025 AT 10:51Flagyl ER’s extended‑release formulation allows a steady plasma level over 24 hours.
This eliminates the peaks and troughs seen with immediate‑release metronidazole.
For bacterial vaginosis and trichomoniasis, the 500 mg once‑daily schedule has been shown to be as effective as the classic three‑times‑daily regimen.
Patients often report better adherence simply because they only need to remember one pill a day.
The cost, while a bit higher than generic metronidazole, is still competitive when compared to tinidazole’s three‑day course.
Side‑effects such as nausea, a metallic taste, and occasional headache remain similar across nitroimidazoles.
The infamous disulfiram‑like reaction with alcohol is still present, so a 48‑hour alcohol‑free window after the last dose is mandatory.
When contraindications to metronidazole exist, clindamycin offers a valuable alternative with broader anaerobic coverage.
However, clindamycin carries a higher risk of Clostridioides difficile infection, which clinicians must monitor.
Doxycycline, while inexpensive and useful for mixed genital infections, requires twice‑daily dosing with food and raises photosensitivity concerns.
Tinidazole’s single‑dose option can be attractive for patients who struggle with multi‑day regimens, but its availability can be limited in rural pharmacies.
Ciprofloxacin excels in urinary tract infections but lacks activity against obligate anaerobes, making it unsuitable for BV.
Insurance coverage in Australia often subsidizes Flagyl ER under the PBS, reducing out‑of‑pocket expense for many patients.
Drug‑drug interactions, such as metronidazole’s effect on warfarin’s INR, demand regular monitoring during therapy.
Ultimately, the choice hinges on the infection type, patient comorbidities, adherence potential, and cost considerations.
harry wheeler
October 29, 2025 AT 08:31Your overview hits the main points the daily pill helps adherence and the side effects stay the same
faith long
November 5, 2025 AT 07:11Don’t be fooled by the notion that price alone dictates the best therapy. The real danger lies in overlooking patient history and blindly prescribing the cheapest option. Flagyl ER may cost a little more, but its once‑daily schedule slashes the risk of missed doses that can fuel resistance. Ignoring the alcohol‑interaction warning is a recipe for disaster and can land patients in the emergency department. If you think clindamycin’s broader coverage justifies its higher C. difficile risk, you are playing with fire. Doxycycline’s cheap price does not excuse the need for strict sun protection measures that many patients ignore. Tinidazole’s single‑dose convenience is irrelevant if the pharmacy can’t stock it, leaving the patient stranded. Ciprofloxacin should never be a fallback for anaerobic infections because it simply won’t work. The bottom line is that clinicians must weigh efficacy, safety, and adherence, not just the sticker price.
Danny Wakefield
November 12, 2025 AT 05:51It’s funny how the pharma giants love to push the “cheap” medals while hiding the real stories about side‑effects and hidden fees. Some say the extended‑release tech in Flagyl ER was kept secret for years until the market demanded a simple pill. The “single‑dose” hype around tinidazole feels like a marketing ploy, but the truth is there are distribution chains that only a few insider groups control. Still, the best thing we can do is stay informed and not let the narrative drive our choices.
Samantha Dean
November 19, 2025 AT 04:31In light of the considerations presented, a judicious selection of antimicrobial therapy necessitates a balanced appraisal of pharmacokinetic advantages, safety profiles, and socioeconomic factors. The extended‑release formulation of metronidazole confers distinct adherence benefits, yet it must be contextualized within the broader therapeutic armamentarium. Moreover, vigilance regarding drug‑drug interactions remains paramount to mitigate iatrogenic complications. Consequently, clinicians are advised to individualize treatment regimens based on comprehensive patient assessments rather than singular market narratives.
Vanessa Peters
November 26, 2025 AT 03:11The drama of antibiotic selection reads like a battlefield where each drug dresses in armor of efficacy while secretly wielding hidden grenades of side‑effects. Flagyl ER strides in as the hero, yet its alcohol‑reactive trait is a silent assassin awaiting the unsuspecting. Tinidazole flashes a flashy single‑dose sword but hides supply chain shadows that can leave patients weaponless. Clindamycin’s broader coverage is a double‑edged blade that slices both infection and gut flora, inviting C. difficile chaos. Doxycycline’s cheap charm conceals a sun‑burned curse for outdoor lovers. Ciprofloxacin, the tough‑guy fluoroquinolone, threatens tendons and cartilage with every dose. The ultimate strategist must parse these hidden perils before committing troops to the front line.
Suzan Graafstra
December 3, 2025 AT 01:51When we swallow a pill, we are not merely ingesting chemicals; we are engaging in an intimate dialogue with the microscopic world that inhabits us. The choice between Flagyl ER and its counterparts becomes a reflection of our desire to harmonize convenience with caution. Does the ease of a once‑daily tablet symbolize humanity’s pursuit of simplicity, or does it mask the complexity of microbial ecosystems? Perhaps the true wisdom lies in acknowledging that every antimicrobial act reshapes the delicate balance within. In this perpetual dance, humility becomes the most potent prescription.
Kripa Mohamed
December 10, 2025 AT 00:31Just remember to finish the whole course and stay away from booze for two days after the last dose – that’s the real trick.