Beta-blocker: What they do, who needs them, and how to stay safe
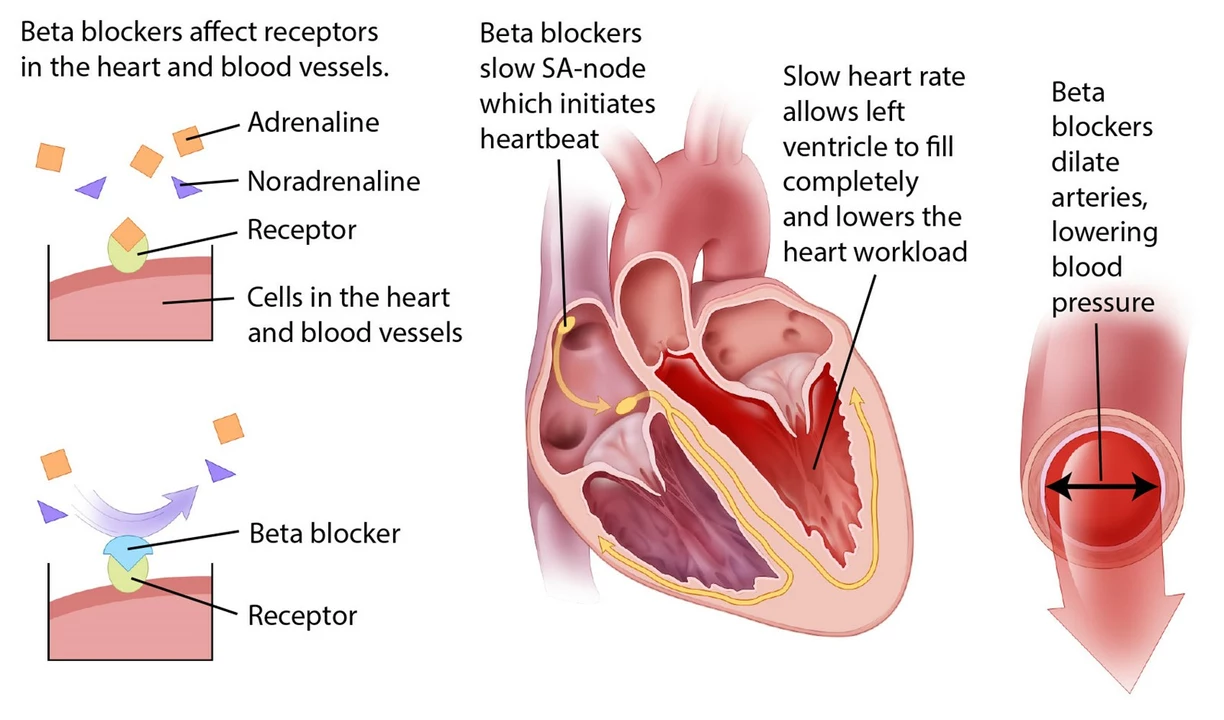
Beta-blockers are a group of medicines that slow your heart and lower blood pressure. Doctors prescribe them for high blood pressure, certain heart rhythm problems, chest pain (angina), heart failure, some tremors, migraine prevention, and performance anxiety. They work by blocking the effects of adrenaline on the heart and blood vessels, which calms things down fast.
How beta-blockers work and common types
There are two main kinds: non-selective and cardioselective. Non-selective ones, like propranolol, affect the whole body—heart and lungs. Cardioselective types, such as metoprolol, atenolol, bisoprolol, and nebivolol, mostly target the heart. That makes them safer for people with mild lung problems, but caution is still needed.
Examples you’ll often hear about: propranolol (used for tremor, anxiety, migraine), metoprolol (blood pressure, heart rhythm, heart failure), atenolol (blood pressure), and bisoprolol or nebivolol (heart failure or long-term heart care). Each drug behaves a bit differently, so your doctor picks the right one for your condition and other medicines you take.
Safety, side effects, and practical tips
Common side effects include tiredness, cold hands or feet, slower pulse, and dizziness when standing up fast. Less common but serious effects are worsening asthma, fainting, very slow heart rate, or new memory problems. If you have asthma, COPD, or serious circulation issues, mention that to your doctor—some beta-blockers can make breathing worse.
Drug interactions matter. Beta-blockers can interact with calcium channel blockers, certain antidepressants, and medicines for diabetes. They can mask low blood sugar symptoms, so people with diabetes should monitor glucose more closely. Always tell your prescriber about every medication, including supplements.
Never stop a beta-blocker suddenly. Stopping quickly can raise blood pressure or cause chest pain. If you need to stop, your doctor will lower the dose slowly over days or weeks. If you miss a dose, take it when you remember unless it’s almost time for the next one—don’t double up.
Thinking about buying beta-blockers online? Use licensed pharmacies that require a prescription, show contact info, and have clear safety policies. Avoid sites offering prescription drugs without a prescription or at unrealistically low prices. If unsure, read pharmacy reviews and check for a proper pharmacy license in the country where they operate.
Questions to ask your doctor: Is this beta-blocker the best option for my condition? What side effects should I watch for? How will this interact with my other meds or health issues? When should I call for help? Clear answers will make taking the drug safer and less stressful.
Beta-blockers are powerful and useful when used correctly. With the right drug choice, dose, and medical follow-up, most people get good results and fewer symptoms. If anything feels off, contact your healthcare provider—don’t guess.
Atenolol and Weakness: Is It a Side Effect?
- 19 Comments
- Apr, 28 2023
I recently came across some information about Atenolol, a medication commonly prescribed for high blood pressure and heart issues. It seems that some users have reported experiencing weakness as a side effect. After doing some research, I've found out that weakness is indeed listed as a potential side effect of Atenolol. If you're taking this medication and experiencing weakness, it's important to discuss this with your healthcare provider. They can help determine if it's related to the medication and suggest possible alternatives or adjustments to your treatment plan.