Side effects: what to expect and when to act
Almost every medicine can cause side effects. Some are mild and go away fast, others need attention right away. This page helps you spot the difference, manage common reactions, and find reliable info — without the jargon.
How to tell if a side effect is serious
Watch for sudden or severe symptoms. Stop and call emergency services if you see: trouble breathing, swelling of face or throat, severe rash with blisters, fainting, chest pain, or seizures. For less dramatic but worrying signs — fast heartbeat, high fever, sudden mood or behavior changes, or new severe pain — contact your doctor or pharmacist the same day.
Timing matters. A reaction that starts right after a dose is more likely to be the drug. But some side effects show up after weeks. If something feels off after starting or changing a med, don’t ignore it.
How to reduce or manage common side effects
Simple steps often help. Nausea? Take the medicine with food or at bedtime, if the leaflet allows. Drowsiness? Avoid driving or heavy machinery until you know how the drug affects you. Upset stomach? Try smaller, more frequent meals and stay hydrated. Mild skin irritation? Stop using the product and ask your provider if an alternative exists.
Don’t stop certain meds suddenly. Drugs for seizures, some heart conditions, and some mental health drugs can cause complications if stopped abruptly. If you want to stop or switch, plan it with your prescriber so they can taper you safely.
Check interactions. New supplements, over-the-counter painkillers, or herbal remedies can change how a prescription drug works. Use a pharmacist or a trusted interaction checker (FDA, NHS, or your national health agency) before mixing medicines.
Where to get reliable side-effect info: read the patient leaflet that comes with the medicine, ask your pharmacist, or check official sources like FDA, EMA, or NHS pages. Our site has focused articles covering drug-specific side effects — for example, check pieces on Strattera, Tamiflu, Nasonex, lamotrigine in pregnancy, and ibuprofen’s heart effects for real-world context and tips.
If a side effect affects your daily life, keep a short log: what happened, when it started, dose, and other meds or foods you had. That makes conversations with your doctor much clearer and speeds up finding a solution.
Finally, report serious or unexpected reactions. In the US you can use FDA MedWatch; other countries have similar systems. Reporting helps regulators spot risks and protects other patients.
Questions about a specific drug? Browse our tag results to find in-depth guides and user-friendly breakdowns on side effects for many common medicines. And if you’re unsure, ask your pharmacist — they’re trained to help you weigh risks and benefits.
Dexamethasone vs Prednisone: Which Steroid Is Stronger and Safer?
- 9 Comments
- Feb, 22 2026
Dexamethasone and prednisone are both powerful steroids, but dexamethasone is 9-10 times stronger and lasts longer. Learn when each is best, how side effects differ, and why doctors choose one over the other.

Lab Monitoring Calendars: Staying Ahead of Side Effects
- 8 Comments
- Jan, 27 2026
Lab monitoring calendars help prevent dangerous side effects from medications like clozapine, lithium, and warfarin by tracking blood levels and symptoms on a schedule. Learn what tests you need, when, and how to stay on track.

Ethinyl Estradiol Guide for Women: Benefits, Risks, Dosage & Side Effects
- 9 Comments
- Oct, 26 2025
A thorough guide on ethynyl estradiol for women, covering how it works, dosage, benefits, side effects, risks and FAQs to help you decide.
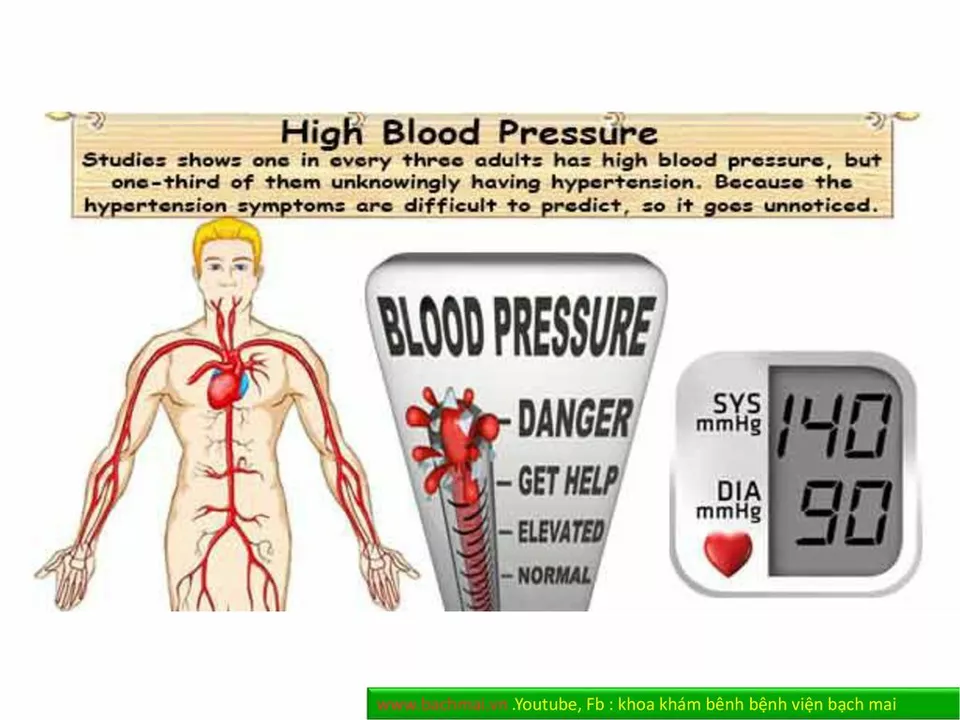
Celecoxib and blood pressure: What you need to know
- 20 Comments
- Apr, 30 2023
As a blogger, I recently came across some important information about Celecoxib and its effects on blood pressure that I wanted to share with my readers. Celecoxib is a type of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that is commonly used to treat pain and inflammation in conditions like arthritis. However, it's crucial to know that Celecoxib may cause an increase in blood pressure, especially for those with a history of hypertension. If you're on this medication, it's essential to monitor your blood pressure regularly and consult with your healthcare provider if you notice any significant changes. It's always best to stay informed and take necessary precautions when it comes to our health.

